Fleas are more than just a nuisance for our canine companions—they’re persistent parasites that can cause discomfort and health issues (including tapeworms, yuck!) if left unchecked. As responsible pet owners, understanding the signs of flea infestations, knowing how to treat them effectively, and implementing preventive measures are necessary. Fleas on dogs are gross, and if you’ve landed on this post, you probably have questions about these tiny little bugs!
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the symptoms of fleas on dogs, discuss treatment options, and outline preventive strategies to help keep your furry friend flea-free and healthy. Whether you’re dealing with a current infestation or looking to safeguard your pet from future flea encounters, this resource aims to provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective flea management!

What are the Symptoms of Fleas on Dogs?
The symptoms of fleas on dogs can vary, but common signs to look out for include:
- Excessive Scratching and Biting: If your dog is constantly scratching, biting, or licking certain areas of their body, especially around the base of the tail, neck, or groin area, it may indicate flea bites.
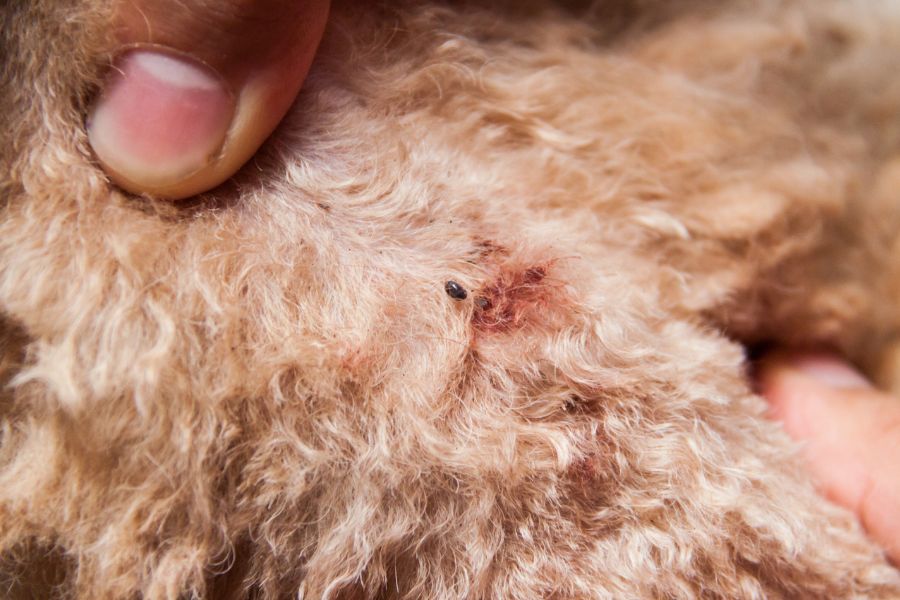
- Redness and Irritation of the Skin: Flea bites can cause redness, inflammation, and small raised bumps on the skin. In severe cases, flea allergy dermatitis (FAD) can develop, leading to intense itching, hair loss, and skin infections.
- Presence of Flea Dirt (Feces) on the Fur: Flea dirt, which looks like small black specks or pepper flakes, is flea feces. You may notice it on your dog’s fur, particularly in areas where fleas are most active.
- Restlessness and Irritability: Infested dogs may exhibit behavioral changes such as restlessness, irritability, and difficulty sleeping due to discomfort caused by flea bites.
- Loss of Appetite: Some dogs may experience a decrease in appetite or reluctance to eat due to the discomfort associated with flea infestations.
- Excessive Grooming: Dogs may groom themselves excessively in an attempt to relieve itching caused by flea bites. This can lead to hair loss, irritated skin, and the formation of hot spots.
Many people mistake these symptoms for food allergies and switch their pet’s food looking for a solution. However, in many cases, the dog is suffering from fleas or mite bites and irritation!
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, especially during warmer months, or if they have been in contact with other animals or infested environments, see a veterinarian.
Read on for our tips to reduce flea infestations, soothe irritated skin, and prevent them from coming back.
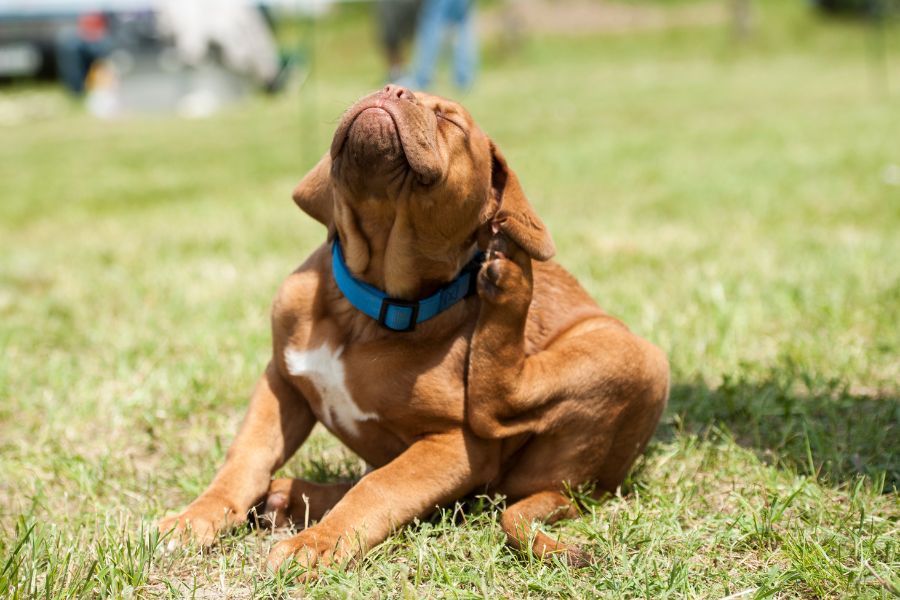

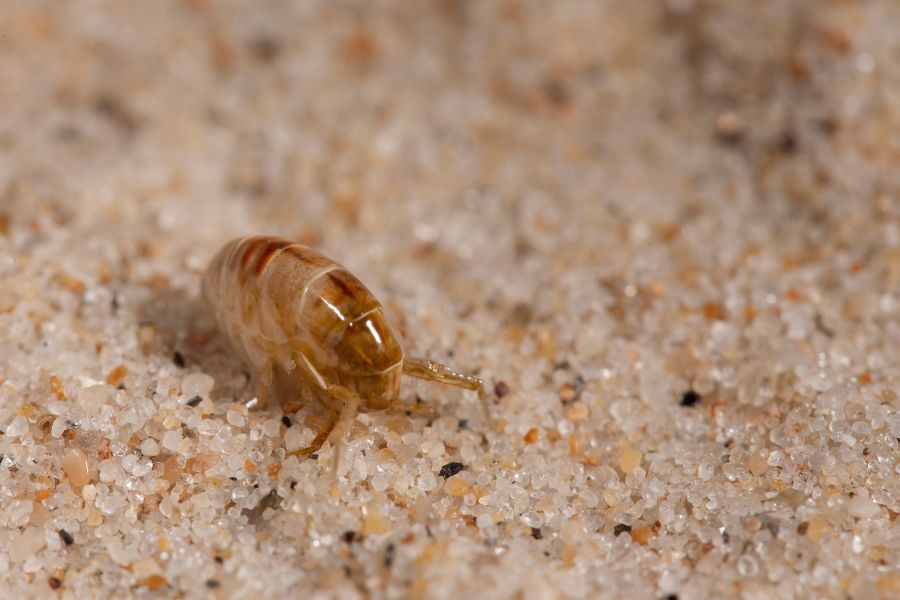
What Do Fleas on Dogs Look Like?
Fleas on dogs are small, wingless insects with flattened bodies that are well-adapted for moving through fur. They are typically reddish-brown in color and measure about 1-3 millimeters in length. When viewed up close, fleas appear narrow from side to side and elongated from top to bottom, giving them a flattened appearance.
While adult fleas are relatively easy to see, they are adept at moving quickly through the dog’s fur, making them sometimes challenging to spot, especially in dogs with thick or dark coats. However, you may be able to detect fleas by parting your dog’s fur and examining areas where fleas commonly hide, such as around the neck, ears, groin, and base of the tail.
Additionally, you may notice flea dirt, which looks like small black specks or pepper flakes, on your dog’s fur. This “dirt” is flea feces and is a telltale sign of flea infestation.
It’s essential to regularly check your dog for fleas, especially if they seem uncomfortable, suffer from allergy-like symptoms, spend time outdoors, or interact with other animals. Early detection and prompt treatment can help prevent flea infestations from becoming more severe and causing discomfort for your pet.
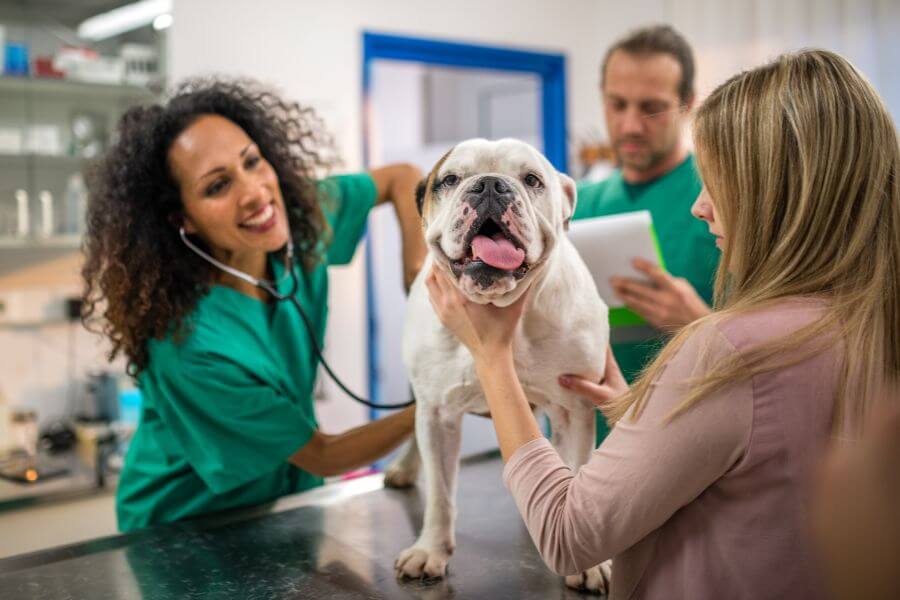
The Best Veterinary Flea Treatment for Dogs
Whether you like it or not, most flea infestations require something stronger than home remedies. There is a lot of misinformation about the safety of flea and tick medications, however, these concerns are largely unfounded.
All medications, including home remedies for fleas, can come with side effects. However, failing to treat fleas on a dog can result in health problems that are much, much worse.
Determining the best veterinary flea treatment for dogs depends on various factors, including the dog’s age, weight, health status, lifestyle, and the severity of the flea infestation. Here are some highly effective veterinary flea treatments commonly recommended by veterinarians:
- Prescription Flea Medications: Veterinarians often prescribe oral flea medications that contain active ingredients such as lufenuron, spinosad, afoxolaner, fluralaner, or sarolaner. These medications are available in chewable tablets or flavored soft chews and work systemically to kill fleas on contact or prevent flea reproduction. Examples include Comfortis, NexGard, Bravecto, and Simparica.
- Topical Spot-on Treatments: Topical spot-on treatments are applied directly to the skin, typically between the dog’s shoulder blades, and provide long-lasting protection against fleas and ticks. They contain ingredients like imidacloprid, fipronil, selamectin, or permethrin. Examples include Frontline Plus, Advantage II, Revolution, and Vectra 3D.
- Flea Collars: Veterinary-recommended flea collars contain active ingredients like imidacloprid, flumethrin, or deltamethrin and provide continuous protection against fleas and ticks for several months. Seresto is a popular veterinary-recommended flea collar known for its effectiveness and longevity.
- Prescription Flea Shampoos and Sprays: In cases of severe flea infestations or allergies, veterinarians may prescribe medicated flea shampoos or sprays containing ingredients like pyrethrins, permethrin, or selamectin. These products provide immediate relief by killing fleas on contact and soothing irritated skin.
When selecting a veterinary flea treatment for your dog, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian to determine the most appropriate option based on your dog’s specific needs and circumstances. Additionally, follow the manufacturer’s instructions and dosage recommendations carefully to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the flea treatment.
Regular veterinary check-ups and flea prevention measures are essential for maintaining your dog’s health and well-being.

Natural Flea & Tick Treatment For Dogs
Natural flea and tick treatments can be effective for some dogs, but their efficacy may vary depending on factors such as the severity of the infestation, the dog’s sensitivity, and the specific products used.
While a home remedy for fleas may not offer the same immediate and potent results as veterinary products such as Capstar and Advantage II, many pet owners believe them to be safer and more environmentally friendly.
Note that essential oils (commonly used in “natural” flea and tick treatments) are chemicals that can be toxic to dogs. There is a lot more to consider than Earthy marketing!
Here are a few natural flea and tick treatments that can be helpful. Major infections require veterinary treatment (there is no getting around this).
- Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) Spray: Mix equal parts of water and apple cider vinegar in a spray bottle and apply it to your dog’s fur, avoiding sensitive areas like eyes and nose. The acidity of ACV repels fleas and ticks and soothes irritated skin.
- Diatomaceous Earth (DE): Food-grade diatomaceous earth is a fine powder made from fossilized algae. DE works by dehydrating and killing fleas and ticks upon contact. Read our blog post on the safety and efficacy of DE against fleas, as there are special considerations.
- Wondercide Flea & Tick Spray: this commercially available natural solution contains pet-safe essential oils to deter bugs. If you use anything with essential oils, stick to a well-known product like this one.
- Regular Grooming and Cleaning: Regularly groom your dog with a flea comb to remove fleas and ticks manually. Wash your dog’s bedding and vacuum your home frequently to eliminate flea eggs and larvae from the environment.
While natural flea and tick treatments can be effective, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian before starting any new regimen, especially if your dog has existing health conditions or if you’re unsure about the safety of certain ingredients. Additionally, monitor your dog for any signs of sensitivity or adverse reactions to natural products and discontinue use if necessary.
- Repellent vs. Killer: Natural treatments often work as repellents rather than outright killers of fleas and ticks. They may help deter pests from latching onto your dog but may not eliminate existing infestations as quickly as chemical treatments.
- Frequency of Application: Natural treatments may require more frequent application compared to veterinary products to maintain their effectiveness.
- Environmental Management: Combining natural treatments with environmental control measures, such as regular grooming, washing bedding, and vacuuming, can enhance their effectiveness by targeting fleas and ticks at various stages of their life cycle.
- Individual Variation: Some dogs may respond well to natural treatments, while others may not experience significant relief. Factors such as the dog’s breed, age, health status, and environmental exposure play a role in determining treatment effectiveness.
- Consistency and Persistence: Consistent and persistent use of natural treatments is key to achieving optimal results. It may take time to see improvements, and regular maintenance is necessary to prevent re-infestation.

Does Dawn Dish Soap Kill Fleas on Dogs?
Dawn dish soap may temporarily kill fleas on dogs, it is not considered safe for use on pets due to its harsh ingredients and potential for skin irritation. Despite its effectiveness in killing fleas, using Dawn dish soap on dogs can strip their skin of natural oils, leading to dryness, irritation, and potential long-term skin issues.
Instead of relying on Dawn dish soap, it’s recommended to use veterinary-approved flea treatments and shampoos specifically formulated for dogs. These products are designed to effectively kill fleas while being gentle on your dog’s skin and coat.
If you’re dealing with a flea infestation on your dog, consult with your veterinarian for safe and effective flea treatment options tailored to your pet’s individual needs. They can recommend the most appropriate flea control products and provide guidance on how to use them safely and effectively.
Is Garlic Effective Flea Control For Dogs?
While some pet owners believe that garlic can be effective for flea control in dogs, there is limited scientific evidence to support its efficacy, and its safety remains a subject of debate among veterinarians.
Garlic contains compounds called thiosulfates, which, when ingested in large quantities, can be toxic to dogs. Ingesting garlic in high doses can lead to a condition called hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed, potentially resulting in weakness, lethargy, pale gums, and even death in severe cases.
While the amount of garlic typically used in homemade flea remedies is unlikely to cause immediate harm, long-term or repeated exposure to garlic can pose health risks to dogs. Additionally, the effectiveness of garlic as a flea repellent or treatment is questionable, as fleas may not be significantly deterred by the consumption of garlic.
Instead of relying on garlic for flea control, it’s recommended to use veterinary-approved flea preventatives specifically formulated for dogs. These products are safe, and effective, and provide comprehensive protection against fleas, ticks, and other parasites. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, maintaining a clean living environment, and minimizing exposure to infested animals and environments are essential components of a comprehensive flea control strategy.
If you have concerns about fleas or are considering alternative flea control methods for your dog, it’s important to consult with your veterinarian. They can provide guidance on safe and effective flea control options tailored to your pet’s individual needs and circumstances.

Diseases Caused by Fleas on Dogs
Fleas on dogs can transmit various diseases and health issues, posing risks to both pets and humans. Some of the diseases caused by fleas on dogs include:
- Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD): FAD is a common allergic skin reaction in dogs caused by flea bites. Dogs with FAD may experience intense itching, hair loss, redness, and skin irritation. Continuous scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections and exacerbate the condition. Many pet owners mistakenly misdiagnose this condition as “food allergies”.
- Anemia: Severe flea infestations can cause anemia in dogs, especially in young puppies or small breeds. Fleas feed on blood, and heavy flea infestations can lead to significant blood loss over time, resulting in weakness, lethargy, pale gums, and even collapse in severe cases.
- Tapeworm Infection: Fleas serve as intermediate hosts for tapeworms, parasitic worms that can infect dogs when they ingest fleas during grooming. Symptoms of tapeworm infection in dogs may include scooting, weight loss, vomiting, and the presence of rice-like segments (tapeworm segments) in the feces or around the anus.
- Hemoplasmosis: Fleas can transmit hemotropic mycoplasmas, bacterial organisms that infect red blood cells, leading to hemoplasmosis in dogs. Symptoms may include anemia, weakness, lethargy, fever, and jaundice.
- Bacterial Infections: Flea bites can introduce bacteria into a dog’s skin, leading to bacterial infections such as impetigo or cellulitis. These infections may cause skin redness, swelling, pain, and the formation of pus-filled lesions.
- Vector-Borne Diseases: Fleas can transmit various vector-borne diseases to dogs, including:
- Bartonellosis: Bartonella bacteria transmitted by fleas can cause bartonellosis in dogs, leading to fever, lethargy, swollen lymph nodes, and potentially more severe symptoms.
- Murine Typhus: Fleas infected with Rickettsia typhi bacteria can transmit murine typhus to dogs, resulting in fever, lethargy, joint pain, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
- Cat Scratch Disease: Fleas can transmit Bartonella henselae bacteria to dogs, causing cat scratch disease, which may present with fever, swollen lymph nodes, and flu-like symptoms.

Where Do Dogs Get Fleas From?
Dogs can get fleas from various sources, including:
- Other Animals: Dogs can pick up fleas from direct contact with other infested animals, such as stray dogs, cats, rodents, or wildlife. Fleas can easily transfer from one animal to another during social interactions, playing, or grooming.
- Environment: Flea eggs, larvae, pupae, and adult fleas can be present in outdoor environments, including yards, parks, and wooded areas. Dogs can inadvertently pick up fleas while exploring or spending time outdoors, especially in areas frequented by wildlife or other infested animals.
- Indoor Spaces: Fleas can hitch a ride into indoor environments on clothing, shoes, or belongings and establish infestations in homes. Once indoors, fleas can thrive in carpets, upholstery, bedding, and cracks and crevices, providing ample opportunities to infest dogs and other pets.
- Flea Infested Items: Dogs can acquire fleas from infested items such as bedding, blankets, carpets, and furniture. Flea eggs, larvae, and pupae may hide in these items and emerge as adult fleas, leading to infestations in dogs and their living spaces.
- Grooming Facilities or Boarding Kennels: Dogs may come into contact with fleas while visiting grooming facilities, boarding kennels, or pet daycare centers where infested animals are present. Poor hygiene practices or inadequate flea control measures in these environments can contribute to the spread of fleas among dogs.
- Travel: Traveling to areas with higher flea populations or staying in accommodations where infested animals have been present can increase the risk of dogs encountering fleas.
To prevent flea infestations, it’s essential to regularly inspect dogs for fleas and ticks, use veterinary-approved flea preventatives year-round, practice good hygiene, maintain a clean living environment, and minimize exposure to infested animals and environments. Additionally, consulting with a veterinarian for personalized flea control recommendations can help protect dogs from the discomfort and health risks associated with flea infestations.











