Learning how to use home remedies for arthritic dogs can be one of the best things you can do for your pet. Arthritis is a common condition in dogs, and it can be painful and debilitating. But with the right home remedies, you can help your dog feel better and ease his pain.
There are a number of home remedies for arthritic dogs that you can try that can help with joint pain associated with dog arthritis.


Do home remedies for arthritic dogs actually work?
Do you have an arthritic dog? If so, you know just how painful and debilitating the condition can be. Dogs with arthritis often have trouble getting around, climbing stairs, and playing fetch. Fortunately, there are a number of home remedies that can help ease your dog’s pain and improve his mobility.
How do I know if my dog has arthritis?
The most common signs of arthritis in dogs are:
- Limping or lameness
- Difficulty rising from a lying down position
- Decreased activity level
- Reluctance to jump, run or climb into the car
- Stiffness or acting ‘sore’
Dogs have a keen ability to mask pain, so it is important to be aware of any changes in your dog’s activity level or mobility. If you notice any of the above signs, make an appointment with your veterinarian. They will be able to confirm whether or not your dog has arthritis and recommend a treatment plan.
There is no cure for arthritis, but there are a number of treatments that can help ease your dog’s pain.
What home remedies can I give my dog for arthritis?


Pain relief and pain management is something that pet parents always want to work on with their dog’s joints. If your dog has arthritis pain, there are natural remedies that can help provide pain relief at home.
YOUR DOG’S DIET
One of the most important things to help decrease pain and treat arthritis is a healthy diet.
A diet that is rich in omega-three fatty acids can help to decrease inflammation and pain. Foods like salmon, flaxseed, and pumpkin seeds are all great sources of omega-three fatty acids. You can also give your dog a fish oil supplement. Just be sure to talk to your vet before giving your dog any supplements.
Raw dog food has been known to provide aminos, nutrients and vitamins to ease pain associated with joint disease.
We recommend finding a balanced raw dog food like Raws Paws. Use code HELLODANES10 for 10% off your entire purchase.
PHYSICAL THERAPY
Older dogs tend not to move as often or as much as younger, more spry dogs. Joint inflammation happens more in dog’s muscles when there is less movement, less blood flow, and less muscle.
In order to relieve pain, increase blood flow and help with chronic pain, work on stretches and movement as often as you can.
It is always better to move frequently and for small periods of time with large breed dogs struggling with joint pain, rather than once a day for a long time. A healthy joint needs blood flow to help with chronic pain and keep the area healthy.
WHAT BED IS BEST FOR A BIG DOG WITH ARTHRITIS?
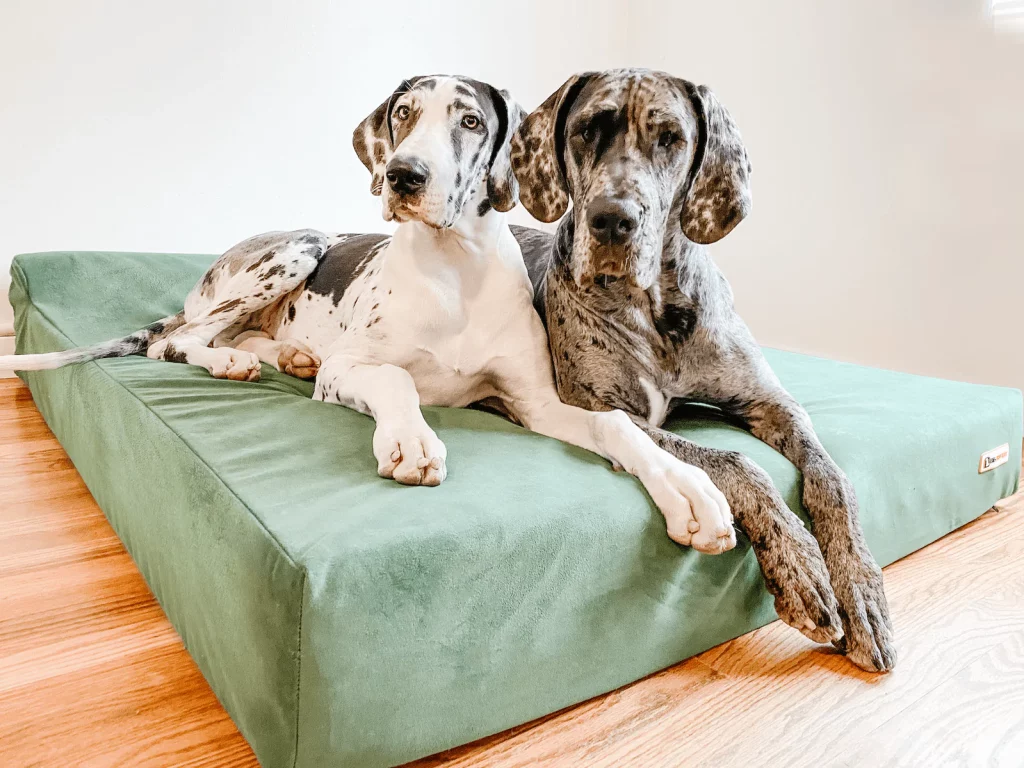

The Big Barker bed is clinically proven to help support dog’s joints. Dogs should not ever rest their legs/joints/shoulders/elbows on the hard surface for extended periods of time.
This can create joint pain and issues like Hygromas.
Big dogs, especially, need a supportive sleeping surface.
We love the Big Barker bed for any dog predisposed to arthritis or joint problems.
Shop here:
EXERCISE
Just like people, dogs need exercise to maintain their health, even if they have arthritis. Exercise is important for all dogs, but especially those with arthritis because it helps increase blood flow to the joints and muscles. It also helps maintain muscle mass and flexibility.
YOUR DOG’S WEIGHT
In order to reduce pain, you should always monitor your dog’s body weight. Aging dogs will have a slowing metabolism.
An overweight dog will have severe pain and pressure on their affected joints.
Relieving pain could be as easy as keeping your dog at a healthy weight. Finding a weight management plan is easy, but sticking with it to keep your dog at a healthy weight is not always easy. Choose a healthy diet and limit your dog’s food to the necessary amount.
| DEADLY RISK OF BEING OVERWEIGHT |
| OVERWEIGHT DOGS IS A HUGE PROBLEM |
| IS YOUR DOG TOO SKINNY? |
| HOW MUCH SHOULD A MALE GREAT DANE WEIGH? |
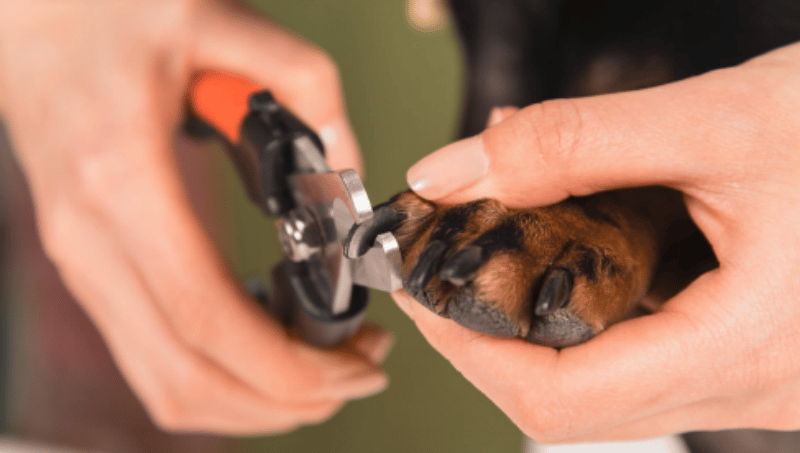
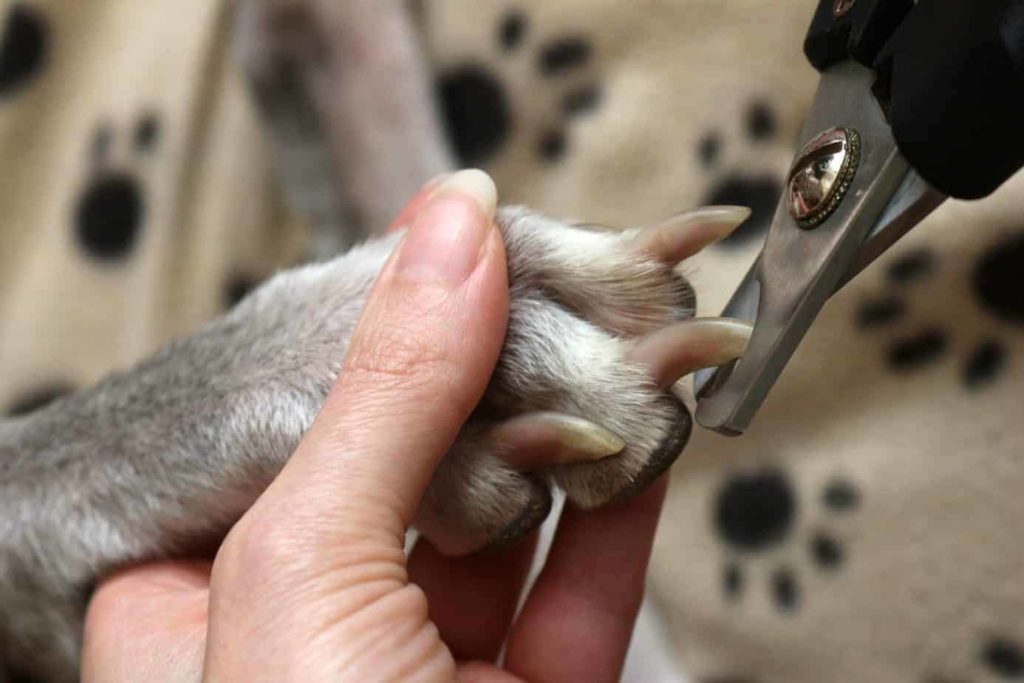
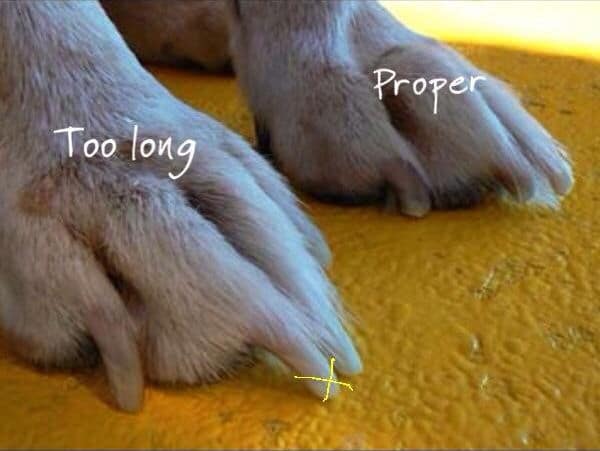
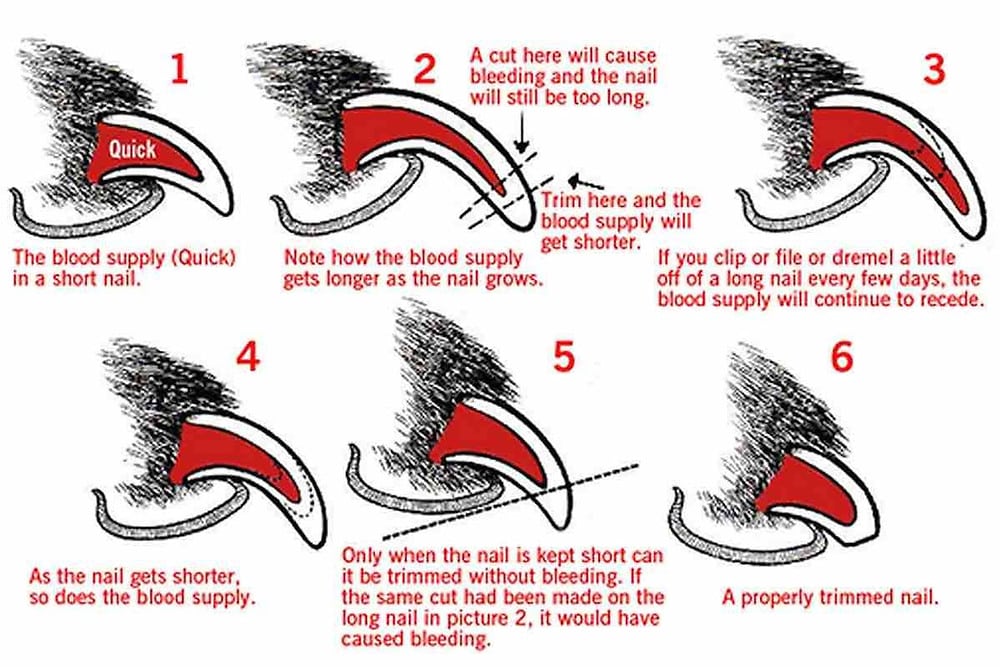
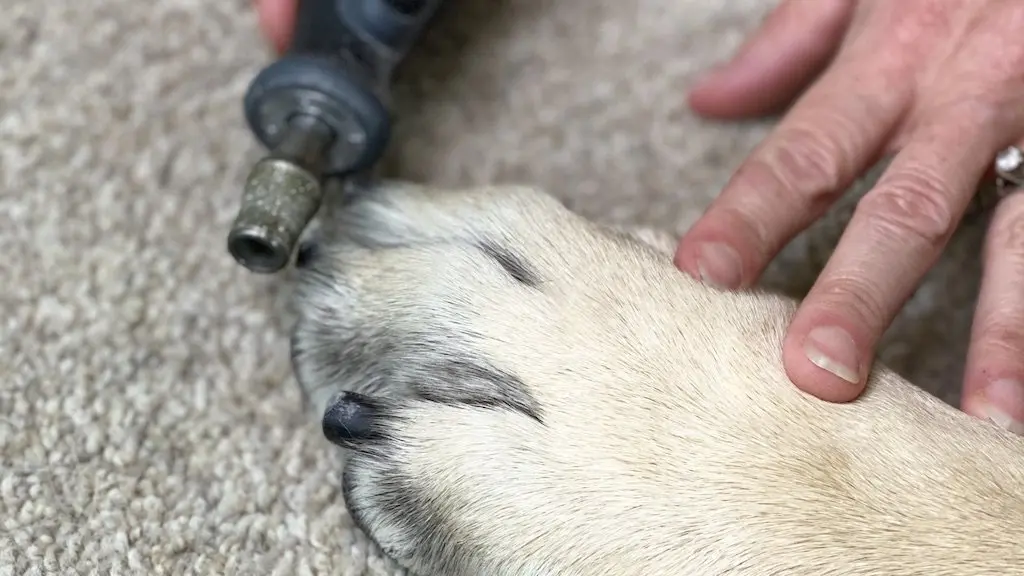
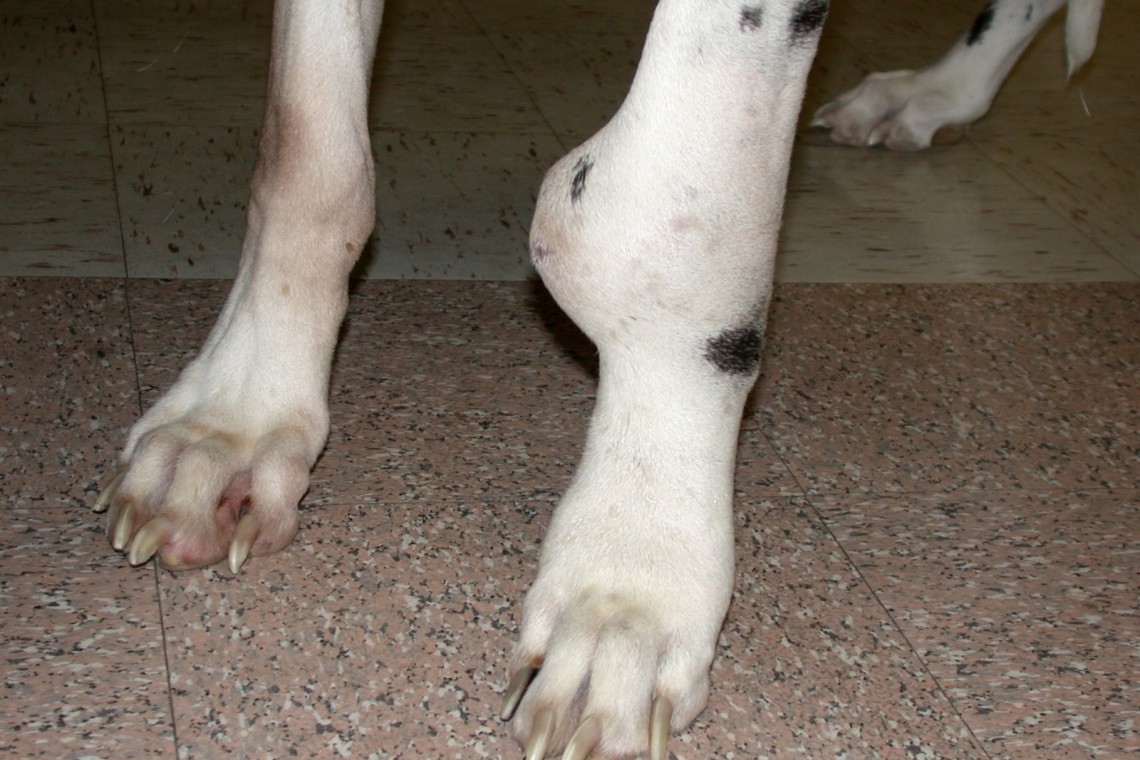
KEEPING YOUR DOGS NAILS SHORT
Keeping your dogs nails short is one way to ensure that their joints do not carry extra pressure or pain.
Long nails can create extra strain and pain for your dog.
Long nails can also cause other issues like foot problems or infection.
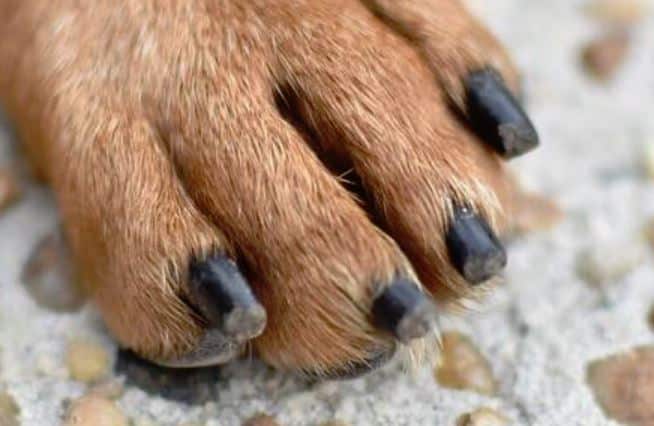



Check out our resources for nail care:
| Great Dane Arthritis |
| The Best Nail Clippers |
| Great Dane Toenail Problems |
| How Often Should You Cut Your Dog’s Nails |
| How to Trim a Puppies Nails |
| What are the Best 7 Clippers? |
What is the best remedy for arthritis in dogs?


Your dog’s health is in nobody’s control but yours.
Between a proper diet, acupuncture treatment, underwater treadmill, gentle massages, anti inflammatory drugs, herbal remedies, pet parents are flooded with ways to treat joint pain for their dog’s arthritis.
There is not one single best remedy to treat joint pain.
However, the best part is that many natural remedies are free or VERY affordable, which means that pet owners can try them out until they find what works for their dogs arthritis.
FREE OF COST NATURAL REMEDIES FOR DOG’S JOINTS:
- Doing physical therapy at home
- Managing their dog’s diet and weight
- Choosing their dog’s food wisely
- Providing massage therapy after a long day
- Taking their dog for short, frequent walks on a variety of surfaces
- Making homemade bone broth
- Taking their dog swimming
Experiment with your dog’s joints and see what works to provide the best pain relief.

Arthritis in Great Danes? Read here.
There are endless possibilities when it comes to treating your dog’s arthritis at home. With a little bit of creativity, you can come up with a plan that works for you and your dog. Just be sure to talk to your vet first before trying any new treatments.
What is the best thing to give an older dog for arthritis?


If you are trying to help increase joint function in a senior dog, the best thing to give them is pain medications in conjunction with any other natural remedy that your dog might take well to.
There are many different types of herbs and supplements on the market that have anti inflammatory properties, so it is important to talk to your veterinarian about which one would be best for your dog. However, for a senior dog, sometimes they need traditional veterinary medicine to help the pain.
Some joint supplements contain glucosamine and chondroitin, which can help to lubricate the joints and decrease developing arthritis.
Our favorites are here:

What natural supplement can I give my dog for arthritis?
Traditional Chinese medicine offers a variety of joint health options.
With traditional herbal medications, you will need to speak with a holistic veterinarian. There are cervical powders that can increase joint health and help joint mobility.
What can I give my dog for joint problems?

If your dog is struggling with joint mobility, consider the following options:
- Fish oil: This is a popular supplement for people and dogs. It can help to reduce inflammation in the body and improve joint health.
- Glucosamine and chondroitin: These supplements are often used together to improve joint health. They can help to lubricate the joints and decrease developing arthritis.
- Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM): This is a sulfur-containing compound that can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- CBD oil: This is a popular natural remedy for many different conditions, including joint pain. It can help to reduce inflammation and provide relief from pain.
- Turmeric: This spice is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. It can be given to dogs in supplement form or added to their food.
- Dog stairs: Dog’s bones bare up to 6x the weight of their body when the dog lands from an upward position, jumping downward. Include options for your dog’s treatment plan that help them not have to jump downward out of the car or off of beds/couches.
- Rugs/Runners: Slippery floors are detrimental to dog arthritis pain.
There are many different options available when it comes to giving your dog joint supplements. Speak with your veterinarian about which one would be best for your dog based on their individual needs.
What diet can I give my dog for arthritis?
For dog arthritis pain relief, you should look for a diet that is going to improve joint mobility.
Nutrients that have been proven in dog’s meals to help dog arthritis pain:
- Omegas: These are found in fish oil and can help to reduce inflammation in the body.
- Glucosamine: This is a compound that can help to lubricate the joints and decrease developing arthritis.
- Chondroitin: This is a compound that can help to lubricate the joints and decrease developing arthritis.
- Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM): This is a sulfur-containing compound that can help to reduce inflammation and pain.
- CBD oil: This is a popular natural remedy for many different conditions, including joint pain. It can help to reduce inflammation and provide relief from pain.
- Turmeric: This spice is known for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Golden Paste: Golden paste is a combination of turmeric, black pepper, and coconut oil. It can be given to dogs in supplement form or added to their food.
- Raw Foods: Raw foods contain enzymes that can help to reduce inflammation.
- Vegetables and Greens: These are a great source of antioxidants and vitamins that can help to reduce inflammation.
- Supplements: There are many different types of supplements on the market that have anti inflammatory properties, so it is important to talk to your veterinarian about which one would be best for your dog.
Dogs with arthritis pain should also be on a diet that helps them maintain a healthy weight.
Should you walk a dog with arthritis?


Many dog owners will notice that as their dog ages they begin to experience pain. In turn, they often LOWER the amount of quality exercise their dog receives.
However, this practice is actually counterintuitive because exercise is an excellent way to combat the effects of arthritis.
The benefits of exercise for a dog with arthritis include:
- Weight management
- Joint lubrication
- Strengthening muscles around joints
- Increased blood circulation and decreased inflammation.
So, yes – you should continue to walk your dog, even if they have canine arthritis! Dog arthritis is a common issue, and can be managed with remedies such as physical therapy, human massage therapy, and pain relief supplements and medications. Exercise is an important part of any dog arthritis treatment plan.
| 7 HEALTH FACTORS TO CONSIDER FOR BIG DOGS |
| FAST REMEDIES FOR ARTHRITIS |
| TOENAIL PROBLEMS |
| SUPPLEMENTS FOR DOGS |
| WHAT IS OFA HEALTH TESTING AND DOES IT MATTER? |
How long can a dog with arthritis live?


Arthritis in dogs is a common condition that can lead to pain and joint deterioration. While there is no cure for arthritis, there are ways to manage the pain and slow the progression of the disease. With proper management, dogs with arthritis can live long and happy lives.
What home remedy can I give my dog for arthritis pain?
One of the best things you can do for arthritis in dogs is weight management. If you see your dog develop arthritis or joint pain, it is crucial to eliminate any excessive weight that they may be carrying.
THE IMPORTANCE OF WEIGHT MANAGEMENT IN DOGS WHO DEVELOP ARTHRITIS
Overweight dogs are more likely to develop arthritis and other joint problems. Excess weight puts additional stress on the joints, which leads to pain and inflammation.
Not only does weight management help to prevent arthritis, but it can also help to relieve pain in dogs who already have the condition.
There are many different ways to help your dog lose weight, including:
- Reducing the amount of food you feed them
- Increasing the amount of exercise they get
- Feeding them a weight-loss dog food
- Adding supplements to their diet that help to boost metabolism or suppress appetite.
- Feeding them the RIGHT amount of food and not giving excessive treats
- Figure out what their ideal weight is so that you know what your goal is
- Monitor all things that they eat, even if it’s just a treat or snack
- Feed more vegetables
If you are unsure about how to best manage your dog’s weight, talk to your veterinarian. They can help!
What can I do for my dog for a natural pain reliever?


Natural remedies are in abundance to work to treat dog arthritis. Although dog arthritis is a prevalent problem, there are things you can do for your dog to help them not feel as much pain.
Laser therapy, acupuncture and other at-home treatment methods are all helpful.
Read more about laser therapy here.
Now, there are even laser therapy machines that can be used at home to help your pup feel their best.
If you are feeling as if your pup is in pain, do not think that you have to let them live that way forever. Talk to your veterinarian and find a pain management plan that works for you both!
READ MORE: